This article is written by Dr A.K.Singal and Dr Ashwitha Shenoy, expert hypospadias surgeons in Navi Mumbai, India. They are rated as the best hypospadias surgeon team in India and this article captures their personal knowledge and expertise in the field of hypospadias.
1. What is hypospadias?
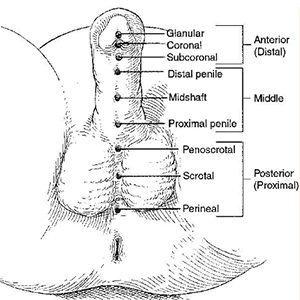
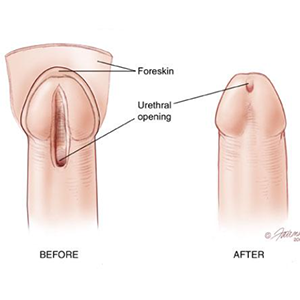
Hypospadias can be easily recognized at birth by a pediatrician due to incomplete prepuce, exposed glans, bent penis (chordee) or abnormal urinary opening itself.
The type of hypospadias is described by where the opening is. The mildest form (glanular) is where the opening is on the glans (see diagram). In moderate hypospadias the opening comes where the glans meets the body of the penis (coronal and sub-coronal). Openings farther back (on the penis itself or at the base of the penis) are the severe varieties. In addition to the hole being in the wrong place, the foreskin is often incompletely formed on the undersurface and looks like a hood on the top. Sometimes the penis is bent downwards (chordee) usually due to tight skin but sometimes due to abnormality of the body of the penis.
Usually, these babies are referred to a Hypospadias Surgeon in the first month of life for proper planning of hypospadias corrective surgery. This referral is very important and should be sent to a surgeon well trained in doing hypospadias repair surgery. Whether it is a Pediatric Urologist, a Pediatric Surgeon or a Urologist, the surgeon should have an interest and dedication in the science and art of management of hypospadias. Pediatric Urology Section of American Academy of Paediatrics Recommends that the results of Hypospadias Surgery are best in hands of surgeons who do atleast 40-50 cases a year. Now over to common questions:
- Is hypospadias common?
Yes. It occurs to some degree in 1 in 150 to 200 boys. In India every year more than 80,000 babies are born with hypospadias. Though it is very common but due to social taboo, lot of people don’t talk about hypospadias. Parents don’t tell their relatives and friends that their child has hypospadias though in today’s day and age hypospadias is very much treatable with excellent surgery results. Lot of these children do not reach the right expert surgeon for best results of surgery.
- Is hypospadias associated with any other abnormalities?
Mild to moderate hypospadias are rarely associated with other abnormalities so no further tests are required. If the hypospadias is very severe or there is also an undescended testis or penile size is very small, then further testing is required. These tests may include ultrasound, MRI, karyotype (chromosome) and hormone tests.
- Why does hypospadias happen?
The urinary pipe called urethra normally forms from a strip of special skin forming itself into a tube on the underside of the penis. The process or urethra formation or closure starts from the bottom closing up rather like a zip fastener pulling closed from the scrotum to the tip of the penis. For some reason the end part of the tube fails to form and remains as a flat plate. The underlying cause is unknown in most cases. There are several theories including increased chemicals in environment which block male hormones (called androgen receptor blockers). When male hormones are blocked, the penis doesn’t develop normally with urethra becoming short and hypospadias is the end result. Hypospadias also runs in families with 5-6% of children having a brother, father or some first degree relative having hypospadias. Also, if the person has hypospadias, there is a 5-6% risk of hypospadias in the future children of the patient. Read detailed article here from our team
- Is surgery required for all hypospadias?
Surgery in hypospadias may be required for 2 reasons:
- To make everything work properly, i.e. to make the urine comes out from the tip and to make the penis straight. Straight penis is important for sexual intercourse.
- For cosmetic reasons.
If the boy can pass urine forwards while standing without spraying in a single stream and the urine opening is near the tip of penis, then the operation is purely cosmetic. However, we see a lot of adults coming in to our hypospadias clinic with psychological issues as they do not feel normal when they have untreated hypospadias. So there is risk of psychosocial adjustments and making normal relationships, if the child is left unoperated. Read detailed blog here
- What is the right age for hypospadias surgery?
Ideal age for surgery in most of the hypospadias is between 6-18 months of age if the child is born full term, is gaining weight well, is healthy, doesn’t have any other major congenital anomalies. If the child is underweight, has major anomalies or is preterm, then the surgery should be delayed till 3-5 years of age. Read a detailed article on right age for hypospadias surgert
- Why are the children with hypospadias operated at such a young age? Why not wait till they are older?
Anesthesia is relatively safe after 6 months of age, that’s why we wait till that age. In infancy the babies are still in diapers, so managing them post-surgery at home is very easy for the parents. The catheter can just drip into the diapers and baby can be sent home the evening of hypospadias surgery or maximum the next day. Further the skin and tissues are very pliable and heal very well at this age. Most importantly, erections and infections are also less of an issue at such a young age. Older kids have painful erections after surgery and also the post operative care may be difficult.
- Will there be any problem in the future regarding married life and children after a hypospadias surgery in childhood?
Most of isolated hypospadias once corrected do not have long-term sequences. Only cases where further investigation is warranted to look for fertility issues are the cases where the hypospadias is very severe, there is associated undescended testis or the gender itself is in question. This can be ascertained by a set of certain investigations which your doctor will explain to you if required.
- What are the usual precautions and care needed before surgery?
Babies are checked for fitness for anesthesia by a pediatrician/ anesthetist. A couple of blood tests may be required. Any history of bleeding/ blood disorder in the family should be asked. The baby should be free from any infection elsewhere (cold, cough, diarrhea, skin infections etc.). Generally, babies are kept empty stomach for 2-4 hours before hypospadias surgery as it is a requirement for anesthesia. Bathing is advisable in the morning of surgery. Read detailed article on pre-operative care before hypospadias surgery
- How long does the hypospadias surgery take?
Surgery time depends upon the severity of the hypospadias. Generally total time spent in the operation room (inclusive of anesthesia time) for a penile hypospadias is between 2-3 hours and it may be 3-4 hours for a complex or a redo or a severe hypospadias surgery.
- What does hypospadias surgery involve?
There are many types of operations designed to repair hypospadias. Essentially the operations we use try to bring the hole up to the correct position on the ‘head’ of the penis (glans), make sure that the penis is straight and repair or remove the foreskin all in one operation. Most of the hypospadias repair operations can be done as one night stay procedure or sometimes even day care procedure (in and out of hospital the same day). Your hypospadias surgeon will explain the type of surgery planned for your child.
- What is a urethral catheter or stent?
The surgeon may decide to leave a catheter tube (stent) into the bladder to drain the urine. This is left in place for 5 to 14 days depending on the type of the operation, and usually simply drains urine into the diaper. A urine bag can be attached for older children or adults who no longer use diapers. We also prescribe mild broad spectrum antibiotics are to prevent an infection due to a stent.
The catheter is used to prevent urine running over the internal stitches and the wound while healing remains dry. When the catheter is removed the child may still find passing urine slightly painful but this gets better in 24 hours. The urine catheter may irritate the bladder causing spasms in about 10% of cases. Hence, we regularly prescribe anti spasmodic medications to relax the bladder and keep the child pain free.
- What is the usual post-operative course after hypospadias surgery?
Babies are usually allowed feeds within 3-4 hours after surgery once they are fully awake and asking for feeds. Initially water and juices are started, if there is no vomiting gradually milk and solids are introduced. Generally, babies are on their usual diet by the evening of surgery. Double Diaper care is taught to the parents by the doctors and the nurses. Medications are explained well and discharge to home happens by evening or morning after.
- When is the follow-up visit scheduled after discharge from hypospadias surgery?
First follow-up visit is generally arranged within 5-7 days after surgery for removal of dressing. For distal hypospadias where a TIP repair has been done, we also remove the catheter at this time. After removal of dressing, an antibacterial ointment is applied 4-5 times a day and at each diaper change. In other repairs or complex surgeries, second visit is arranged at 10-14 days after the day of surgery for removal of catheter. A further checkup is done after 3-4 weeks, 3 months and at one year.
- What are common problems after surgery that we should know about?
- Pain: Most of the time the babies are slightly cranky but manageable. They feel better at home, that is why we try to send them to home as soon as possible. It is also easier for the parents to manage them at home. Further an analgesic (pain-killer) syrup is prescribed to help in pain relief.
- Spasms: Babies may have intermittent spasms due to irritation by the catheter. For this reason, a small dose of bladder relaxant is usually prescribed. The dose may need to be adjusted if cramps still happen.
- Blood spotting in the diaper/ catheter may occur in the first few days. A few drops of the blood are acceptable. In case of continuing ooze, a hospital visit may be required but this is very infrequent.
- Dressing issues: Dressing loosening up may occur in some babies, if it happens during first 2-3 days then a new dressing is placed. After that the dressing is just removed.
- Infection may happen and is the most common cause of the failure of surgery. To prevent this, broad spectrum antibiotic syrup is usually prescribed for 7-10 days. It is vital to prevent stool smearing up the dressing in immediate post-operative period.
- Fistula: Fistula is a small area of breakdown in the operated area leading to sideways leakage of urine. Small, off-centre fistulas may heal in due course of time of the tip of the new urethra is not tight. Others may require repair 6-9 months later. The rate of fistula in experienced hands in penile hypospadias is typically 5%.
- Stenosis/ Stricture: During healing period the new urinary tube may become tight. Mostly this happens at the tip of penis and can be easily managed by daily calibration at home with a small feeding tube. Sometimes, if the repair becomes too tight, then a second surgery may be required.
- How can we improve the outcomes of hypospadias surgery in children?
First Hypospadias Surgery done by a well-trained surgeon is the best single indicator of good long term outcome in Hypospadias. When the first surgery fails especially when done by a untrained surgeon, subsequent hypospadias repairs carry a higher failure rate.
First hypospadias surgery outcomes improve with:
- Proper case selection– There are more than 100 techniques described for hypospadias repair. Every child with hypospadias has a different anatomy. The proper choice of surgical technique based on subtle variations in anatomy is the prime factor influencing surgical outcome of hypospadias treatment.
- Dedicated setup: People (full team- surgeon/ anesthesiologist, nurses, assistants, junior doctors) should be trained in pre-op and post-op management of children for hypospadias surgery.
- Dedicated instruments: Sharp, precise, new, microsurgery instruments dedicated towards only hypospadias treatment lead to better surgical results. These instruments are very delicate and should not be used for other surgeries
- Magnification aids during surgery: Use of proper magnification by wearing maginifying loupes while doing surgery aids in identifying proper tissues and also placing the stitches properly. Also, bleeding can be minimized.
- Protocol based approach: Following same steps over and over in last few years for hundreds of hypospadias surgeries have allowed us to deliver best results of hypospadias surgery.
- Short stay surgery: 95% of children are sent home the day of hypospadias surgery or the morning after surgery thus minimizing infections, poor eating issues and happier kids. This results in better outcomes of hypospadias surgery.
Hypospadias in Children Case gallery:
- Case 1: A boy with distal penile hypospadias – Snodgras urethroplasty (also called Tubularized Incised Plate urethroplasty
- Case 2: Hypospadias with thin urethra – Transverse Island Onlay flap Urethroplasty
- Case 3: A boy with severe hypospadias – Transverse Island Onlay flap Urethroplasty
- Case 4: A boy with scrotal hypospadias- Transverse Island Onlay flap Urethroplasty
- Case 5: A child with severe hypospadias- Prepucial tube urethroplasty
- Case 6: A child with severe hypospadias- Modified koyanagi urethroplasty
- Case 7: Severe hypospadias needing a Staged Urethroplasty- Thiersch Duplay Urethroplasty
- Case 8: Distal penile hypospadias with Penile Torsion- Repair in one stage
- Case 9: A Case of Penoscrotal Hypospadias With Severe Chordee And Shortage Of Skin Managed With Two Stage Surgery
- Case 10: Staged Repair In Proximal Penile Hypospadias – Thiersch Duplay Urethroplasty
- Case 11: Glans Approximation Procedure (One Stage Urethroplasty Repair) For Coronal Hypospadias
- Case 12: Single Stage Hypospadias Repair In A Child With Distal Hypospadias After Circumcision
About Hypospadias Foundation
Hypospadias foundation is the World’s first and only organisation dedicated to care of children and adults suffering from Hypospadias. Founded in Nov 2008, more than 5000 children and adults have found hope and cure at Navi Mumbai India or at the Bahrain Hypospadias Centre. Kids and adults travel from all over India and now more than 25+ countries to Navi Mumbai for state of art treatment, surgery for hypospadias and best results. The unique teamwork allows children with hypospadias to gain the best results in treatment of hypospadias.